What Happens to Abandoned Houses?
Understanding the Phenomenon of Abandoned Houses
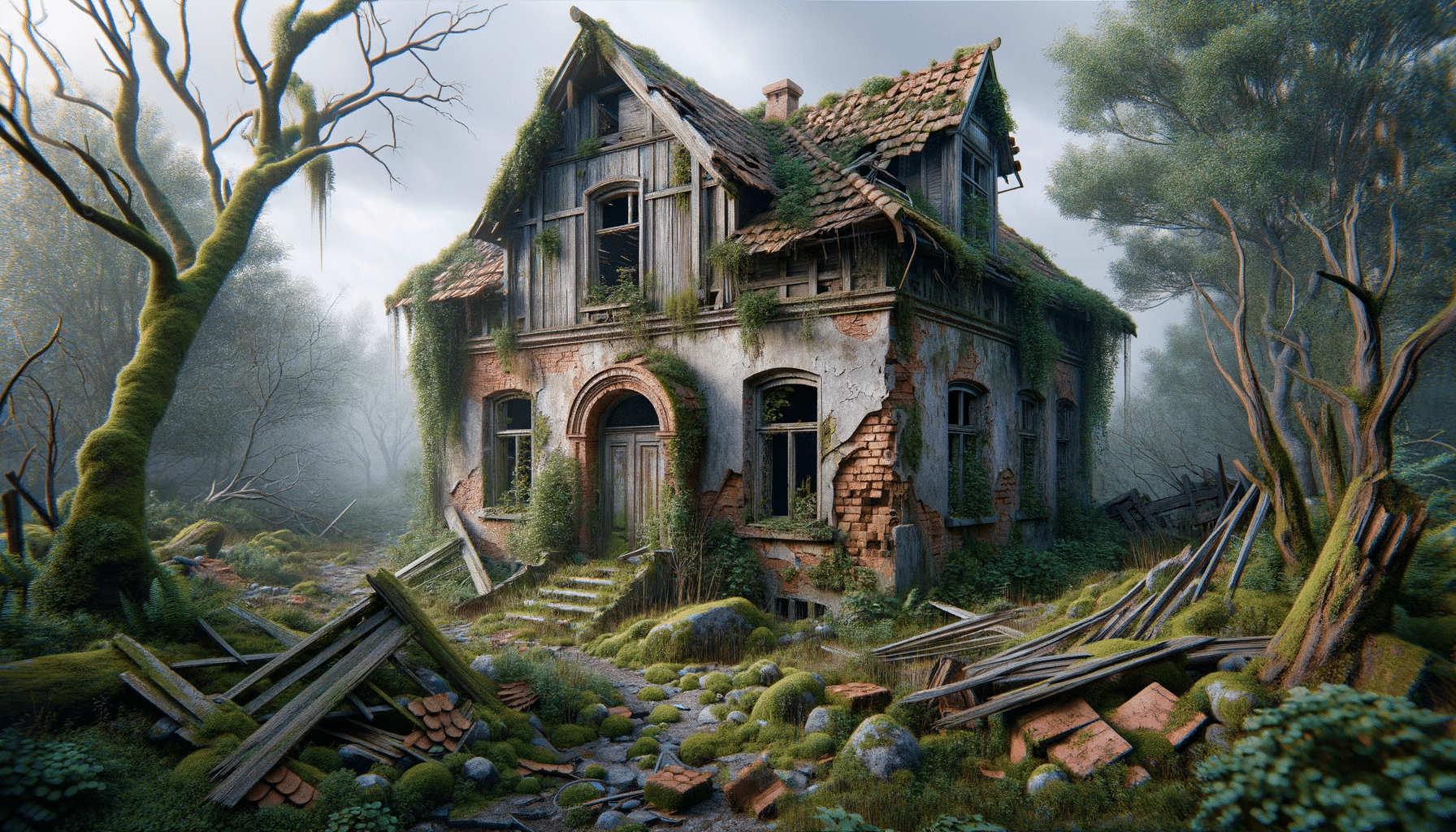
Abandoned houses are a common sight in many parts of the world, and their presence often sparks curiosity and concern. These structures, once homes filled with life and memories, become empty shells due to various reasons. Economic challenges, demographic shifts, and urban development are some of the primary causes that lead to homes being left behind. In some cases, properties are abandoned because of unresolved inheritances, where legal complexities prevent heirs from taking ownership or selling the property. Other times, economic downturns force owners to relocate, leaving their homes behind.
The impact of abandoned houses extends beyond the physical space they occupy. They often become eyesores, affecting the aesthetic value of neighborhoods. Furthermore, they can lead to a decrease in property values for surrounding homes, creating a ripple effect in the local real estate market. Understanding the reasons behind abandonment is crucial for developing effective strategies to manage these properties and prevent further decline.
The Legal and Urban Planning Aspects
In Italy, as in many other countries, the management and recovery of abandoned houses are subject to local regulations. These regulations are designed to address the legal and urban planning challenges that arise from abandoned properties. Local governments may implement special urban planning pathways to facilitate the recovery or redevelopment of these structures.
Legal frameworks often include provisions for identifying and cataloging abandoned properties, determining ownership, and resolving any legal disputes related to inheritance or ownership rights. Urban planning initiatives might involve incentivizing redevelopment projects, offering tax breaks, or providing financial assistance to encourage renovation and reuse of these properties. By addressing the legal and urban planning aspects, communities can transform abandoned houses into valuable assets, contributing to local development and economic growth.
The Economic Impact of Abandoned Houses
The presence of abandoned houses in a community can have significant economic implications. On one hand, these properties represent untapped potential that, if properly managed, can contribute to economic revitalization. On the other hand, they can also be a financial burden, requiring resources for maintenance, security, and potential demolition.
Abandoned houses can lead to a decrease in property values in their vicinity, as they often become targets for vandalism and illegal activities. This devaluation affects homeowners and can deter potential buyers, leading to a stagnant real estate market. However, with strategic interventions, such as converting these properties into affordable housing or community spaces, they can become catalysts for economic growth. By investing in the rehabilitation of abandoned houses, communities can create jobs, attract new residents, and stimulate local businesses.
Social and Cultural Implications
Beyond their economic and legal aspects, abandoned houses also have social and cultural implications. These structures often hold historical and architectural significance, representing a community’s heritage and identity. When left unattended, they can become symbols of neglect and decline, impacting the social fabric of neighborhoods.
However, abandoned houses also present opportunities for cultural and social innovation. Communities can repurpose these spaces for artistic endeavors, cultural events, or social initiatives, fostering a sense of belonging and community pride. By engaging residents in the process of revitalizing abandoned houses, communities can strengthen social ties and promote cultural preservation.
Strategies for Managing Abandoned Houses
Effectively managing abandoned houses requires a multifaceted approach that involves collaboration between government agencies, community organizations, and private stakeholders. Some strategies include:
- Implementing comprehensive property registration systems to identify and monitor abandoned houses.
- Offering financial incentives, such as grants or tax breaks, to encourage property owners to renovate or sell their abandoned homes.
- Developing community-based initiatives that involve residents in the decision-making process for the future of abandoned properties.
- Creating partnerships between public and private sectors to fund and execute redevelopment projects.
- Promoting adaptive reuse of abandoned houses for community-oriented purposes, such as affordable housing or cultural centers.
By adopting these strategies, communities can transform the challenge of abandoned houses into opportunities for growth, development, and revitalization.